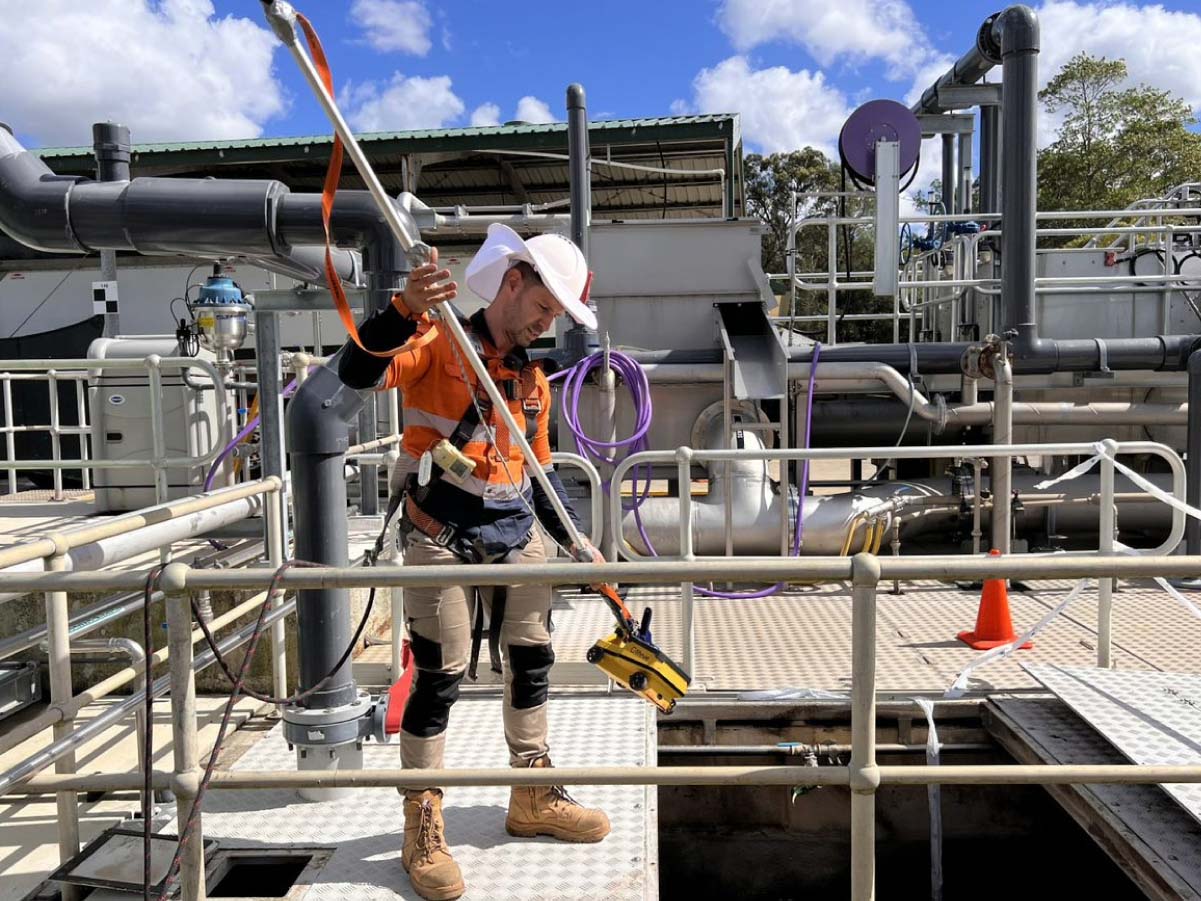
In modern construction, knowing the true condition of concrete structures is critical for safety, compliance, and project success. Non destructive concrete testing (NDT) offers a way to assess strength, durability, and integrity without causing damage.
From bridges and high-rises to car parks and residential developments, this approach is becoming a standard part of quality control and asset management. If you’re involved in construction or building maintenance, understanding how NDT works and why it matters can help you make better decisions.
What Is Non Destructive Concrete Testing?
Non destructive concrete testing is the process of evaluating concrete’s properties without physically altering or damaging the material.
Instead of cutting, coring, or breaking samples, NDT methods use specialised tools and techniques to gather information from the surface or by sending signals into the concrete.
The results can reveal:
- Compressive strength
- Thickness and uniformity
- Presence of cracks or voids
- Location of reinforcement
- Moisture content
- Potential deterioration or corrosion
Why It Matters in Construction
Concrete is the backbone of modern infrastructure – but it’s not immune to wear, weather, or structural stress. Over time, factors like heavy loads, temperature changes, chemical exposure, and poor initial workmanship can impact its performance.
Benefits of NDT include:
- Preserves the structure – Testing doesn’t damage the concrete, so the structure remains intact.
- Saves time and money – Avoids unnecessary demolition or repair.
- Improves safety – Identifies potential hazards before they cause failures.
- Supports compliance – Helps meet Australian Standards and engineering requirements.
- Provides accurate data – Enables informed decision-making during construction, maintenance, or refurbishment.

Common Non Destructive Testing Methods for Concrete
Different NDT methods are used depending on the project stage, site conditions, and required data. Here are some of the most widely used in the construction industry:
1. Rebound Hammer Testing (Schmidt Hammer)
This method measures surface hardness, which can be correlated with concrete compressive strength.
- How it works: A spring-loaded hammer strikes the surface, and the rebound distance is measured.
- Best for: Quick, on-site assessments and comparing areas of a structure.
- Limitations: Results are affected by surface texture and moisture, so they’re often used alongside other tests.
2. Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV)
UPV measures the time it takes for ultrasonic pulses to travel through the concrete.
- How it works: Transducers are placed on the surface; sound waves are transmitted and received.
- Best for: Detecting cracks, voids, and variations in quality.
- Benefits: Non-invasive and effective for assessing large areas
3. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
GPR Scanning uses radar pulses to map what’s inside the concrete.
- How it works: A handheld device sends high-frequency radio waves into the concrete, reflecting back from embedded objects.
- Best for: Locating reinforcement, post-tension cables, and embedded utilities.
- Advantages: Provides detailed subsurface images without drilling.
4. Cover Meter Surveys
These tests locate reinforcement bars and measure the concrete cover (the distance from the surface to the reinforcement).
- How it works: Uses magnetic or electromagnetic sensors to detect metal.
- Importance: Ensuring adequate cover is essential for durability and corrosion protection.
5. Half-Cell Potential Testing
This technique assesses the likelihood of corrosion in steel reinforcement.
- How it works: Measures the electrical potential of the steel through the concrete surface.
- Benefit: Identifies areas at higher risk of corrosion before visible damage appears.
When to Use Non Destructive Concrete Testing
NDT is valuable throughout the construction and maintenance lifecycle:
- Before construction – Testing existing concrete foundations or elements for suitability.
- During construction – Checking quality and consistency as work progresses.
- Post-construction – Verifying compliance before handover.
- Maintenance phase – Monitoring structural health over time.
- Before renovation or demolition – Identifying embedded elements and hazards.
The Role of NDT in Extending Asset Life
Infrastructure is built to last – but without regular monitoring, small issues can turn into expensive problems. NDT allows asset managers to track changes in condition and plan maintenance before damage worsens.
Examples include:
- Bridges – Monitoring for cracks, moisture ingress, and corrosion.
- Commercial buildings – Checking slab thickness and reinforcement location before installing new penetrations.
- Multi-storey car parks – Detecting deterioration from water and de-icing chemicals.
- Heritage structures – Preserving integrity while ensuring safety.
Choosing the Right NDT Approach
The best NDT method depends on your goals, budget, and site conditions. In many cases, multiple methods are combined for a more complete picture.
Factors to consider:
- Type of structure – Slabs, columns, beams, or walls.
- Age and condition – New builds versus ageing infrastructure.
- Access – Open areas versus confined spaces.
- Required accuracy – Quick checks versus detailed engineering data.
Working with an experienced provider ensures the right tools and techniques are used – and that results are interpreted correctly.
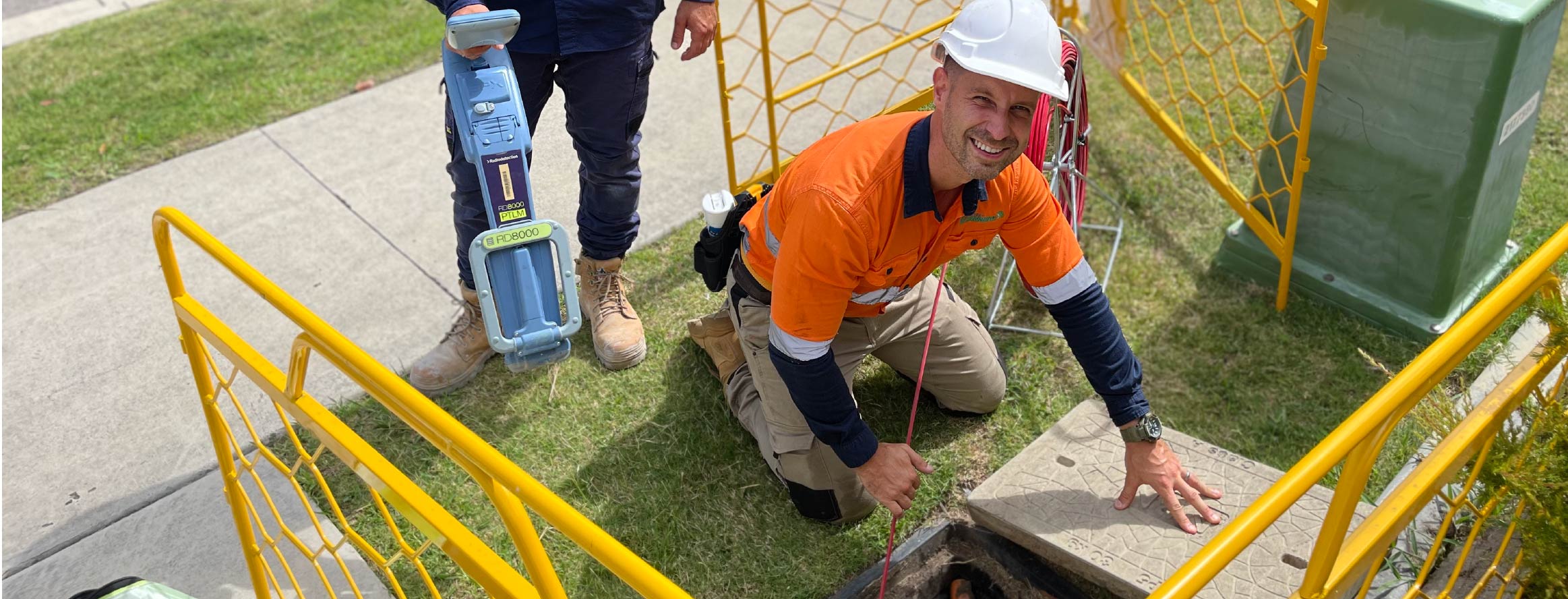

Limitations and Considerations
While NDT offers many benefits, it’s important to understand its limits:
- Some methods provide indirect results that require correlation with destructive testing for full accuracy.
- Surface conditions, moisture, and temperature can affect readings.
- Skilled interpretation is essential – raw data alone can be misleading.
This is why NDT should be performed by qualified professionals familiar with both the technology and the standards governing concrete assessment in Australia.
Why Work With Experts
Non destructive concrete testing is only as good as the people carrying it out. An expert team not only uses the right equipment but also understands construction, engineering, and compliance requirements.
Choosing the right provider means:
- Accurate, reliable data
- Compliance with relevant standards
- Detailed, easy-to-understand reports
- Actionable recommendations for repair, maintenance, or further investigation
If you need accurate, reliable insights into the condition of your concrete structures, our experienced team can help. We use the latest non destructive testing methods to assess strength, durability, and safety – without damaging the structure.
Whether you’re planning new construction, assessing an existing asset, or preparing for refurbishment, we provide the data you need to make confident decisions.
Contact us today to learn more about our non destructive concrete testing services and how we can support your next project.